Web应用安全:攻击、防护与检测
摘要
目前有许多的恶意攻击都是以网站及其用户作为目标,本文将简要介绍在 Web 服务器一侧的安全加固和测试方法。
| 攻击方式 | 防护方式 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| 点击劫持(clickjacking) | X-Frame-Options Header | ----- |
| 基于 SSL 的中间人攻击(SSL Man-in-the-middle) | HTTP Strict Transport Security | ----- |
| 跨站脚本(Cross-site scripting,XSS) | X-XSS-Protection、Content-Security-Policy、X-Content-Type-Options | ----- |
点击劫持(Clickjacking)
点击劫持,clickjacking 是一种在网页中将恶意代码等隐藏在看似无害的内容(如按钮)之下,并诱使用户点击的手段,又被称为界面伪装(UI redressing)。例如用户收到一封包含一段视频的电子邮件,但其中的“播放”按钮并不会真正播放视频,而是被诱骗进入一个购物网站。
针对点击劫持攻击,开放Web应用程序安全项目(Open Web Application Security Project ,OWASP)(非营利组织,其目的是协助个人、企业和机构来发现和使用可信赖软件) 提供了一份指引,《Defending_with_X-Frame-Options_Response_Headers》 。
X-Frame-Options HTTP 响应头是用来给浏览器指示允许一个页面可否在 frame 标签 或者 object 标签中展现的标记。网站可以使用此功能,来确保自己网站的内容没有被嵌到别人的网站中去,也从而避免了点击劫持 (clickjacking) 的攻击。DENY:表示该页面不允许在 frame 中展示,即便是在相同域名的页面中嵌套也不允许。SAMEORIGIN:表示该页面可以在相同域名页面的 frame 中展示。ALLOW-FROM uri:表示该页面可以在指定来源的 frame 中展示。配置如下:
//HAProxy
http-response set-header X-Frame-Options:DENY
//Nginx
add_header X-Frame-Options "DENY";
//Java
response.addHeader("x-frame-options","DENY");
跨站脚本 Cross-site scripting (XSS)
跨站脚本通常指的是通过利用开发时留下的漏洞,注入恶意指令代码(JavaScript/Java/VBScript/ActiveX/Flash/HTML等)到网页,使用户加载并执行攻击者恶意制造的程序。攻击者可能得到更高的权限、私密网页、会话和cookie等各种内容。目前有两种不同的 HTTP 响应头可以用来防止 XSS 攻击,它们是:
- X-XSS-Protection
- Content-Security-Policy
X-XSS-Protection
HTTP X-XSS-Protection 响应头是Internet Explorer,Chrome和Safari的一个功能,当检测到跨站脚本攻击 (XSS)时,浏览器将停止加载页面。配置选项:0 禁止XSS过滤。1 启用XSS过滤(通常浏览器是默认的)。 如果检测到跨站脚本攻击,浏览器将清除页面(删除不安全的部分)。mode=block 启用XSS过滤, 如果检测到攻击,浏览器将不会清除页面,而是阻止页面加载。report=reporting-URI 启用XSS过滤。 如果检测到跨站脚本攻击,浏览器将清除页面并使用 CSP report-uri 指令的功能发送违规报告。参考文章《The misunderstood X-XSS-Protection》:
//HAProxy
http-response set-header X-XSS-Protection: 1;mode=block
//Nginx
add_header X-Xss-Protection "1; mode=block" always;;
浏览器支持情况:
| Chrome | Edge | Firefox | Internet Explorer | Opera | Safari |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Yes) | (Yes) | No | 8.0 | (Yes) | (Yes) |
Content-Security-Policy
内容安全性政策(Content Security Policy,CSP)就是一种白名单制度,明确告诉客户端哪些外部资源(脚本/图片/音视频等)可以加载和执行。浏览器可以拒绝任何不来自预定义位置的任何内容,从而防止外部注入的脚本和其他此类恶意内容。设置 Content-Security-Policy Header:
//HAProxy:
http-response set-header Content-Security-Policy:script-src https://www.google-analytics.com;https://q.quora.com
//Nginx
add_header Content-Security-Policy-Report-Only "script-src https://www.google-analytics.com https://q.quora.com";
MIME-Sniffing
MIME-Sniffing(主要是Internet Explorer)使用的一种技术,它尝试猜测资源的 MIME 类型(也称为 Content-Type 内容类型)。这意味着浏览器可以忽略由 Web 服务器发送的 Content-Type Header,而不是尝试分析资源(例如将纯文本标记为HTML 标签),按照它认为的资源(HTML)渲染资源而不是服务器的定义(文本)。虽然这是一个非常有用的功能,能够纠正服务器发送的错误的 Content-Type,但是心怀不轨的人可以轻易滥用这一特性,这使得浏览器和用户可能被恶意攻击。例如,如通过精心制作一个图像文件,并在其中嵌入可以被浏览器所展示和执行的HTML和t代码。《Microsoft Developer Network:IE8 Security Part V: Comprehensive Protection》:
Consider, for instance, the case of a picture-sharing web service which hosts pictures uploaded by anonymous users. An attacker could upload a specially crafted JPEG file that contained script content, and then send a link to the file to unsuspecting victims. When the victims visited the server, the malicious file would be downloaded, the script would be detected, and it would run in the context of the picture-sharing site. This script could then steal the victim’s cookies, generate a phony page, etc.
//HAProxy
http-response set-header X-Content-Type-Options: nosniff
//Nginx
add_header X-Content-Type-Options "nosniff" always;
SSL Strip Man-in-The-Middle Attack
中间人攻击中攻击者与通讯的两端分别创建独立的联系,并交换其所收到的数据,使通讯的两端认为他们正在通过一个私密的连接与对方直接对话,但事实上整个会话都被攻击者完全控制。例如,在一个未加密的Wi-Fi 无线接入点的接受范围内的中间人攻击者,可以将自己作为一个中间人插入这个网络。强制用户使用HTTP严格传输安全(HTTP Strict Transport Security,HSTS)。 HSTS 是一套由 IETF 发布的互联网安全策略机制。Chrome 和 Firefox 浏览器有一个内置的 HSTS 的主机列表,网站可以选择使用 HSTS 策略强制浏览器使用 HTTPS 协议与网站进行通信,以减少会话劫持风险。

服务器设置下列选项可以强制所有客户端只能通过 HTTPS 连接:
//HAProxy
http-response set-header Strict-Transport-Security max-age=31536000;includeSubDomains;preload
//Nginx
add_header Strict-Transport-Security 'max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload; always;'
暴露 URL (HTTPS > HTTP Sites)
Referrer 信息被广泛用于网络访问流量来源分析,它是众多网站数据统计服务的基础,例如 Google Analytics 和 AWStats,基于Perl的开源日志分析工具。同样的这一特性也会很容易被恶意利用,造成用户敏感信息泄漏,例如将用户 SESSION ID 放在 URL 中,第三方拿到就可能看到别人登录后的页面内容。2014 年,W3C 发布了 Referrer Policy 的新草案,开发者开始有权控制自己网站的 Referrer Policy。但是仅有 Chrome/Firefox 浏览器较新的版本的能够提供支持。
| Feature | Chrome | Firefox | Edge、Internet Explorer、 Opera、Safari |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basic Support | 56.0 | 50.0 | (No) |
| same-origin | (No)1 | 52.0 | (No) |
| strict-origin | (No)1 | 52.0 | (No) |
| strict-origin-when-cross-origin | (No)1 | 52.0 | (No) |
Referrer-Policy选项列表:
- Referrer-Policy: no-referrer //整个 Referer 首部会被移除。访问来源信息不随着请求一起发送。
- Referrer-Policy: no-referrer-when-downgrade //默认选项 //引用页面的地址会被发送(HTTPS->HTTPS),降级的情况不会被发送 (HTTPS->HTTP)
- Referrer-Policy: origin //在任何情况下,仅发送文件的源作为引用地址
- Referrer-Policy: origin-when-cross-origin //对于同源的请求,会发送完整的URL作为引用地址,但是对于非同源请求仅发送文件的源
- Referrer-Policy: same-origin //对于同源的请求会发送引用地址,但是对于非同源请求则不发送引用地址信息。
- Referrer-Policy: strict-origin //在同等安全级别的情况下,发送文件的源作为引用地址(HTTPS->HTTPS)
- Referrer-Policy: strict-origin-when-cross-origin //对于同源的请求,会发送完整的URL作为引用地址
- Referrer-Policy: unsafe-url //无论是否同源请求,都发送完整的 URL(移除参数信息之后)作为引用地址。
我们必须确保用户从全 HTTPS 站点跳转到 HTTP 站点的时候,没有中间人可以嗅探出用户实际的 HTTPS URL,Referrer Policy 设置如下:
//HAProxy
http-response set-header Referrer-Policy no-referrer-when-downgrade
//Nginx
add_header Referrer-Policy: no-referrer-when-downgrade
| Source | Destination | Referrer (Policy :no-referrer-when-downgrade) |
|---|---|---|
| https://test.com/blog1/ | http://test.com/blog2/ | NULL |
| https://test.com/blog1/ | https://test.com/blog2/ | https://test.com/blog1/ |
| http://test.com/blog1/ | http://test.com/blog2/ | http://test.com/blog1/ |
| http://test.com/blog1/ | http://example.com | http://test.com/blog1/ |
| http://test.com/blog1/ | https://example.com | http://test.com/blog1/ |
| https://test.com/blog1/ | http://example.com | NULL |
测试
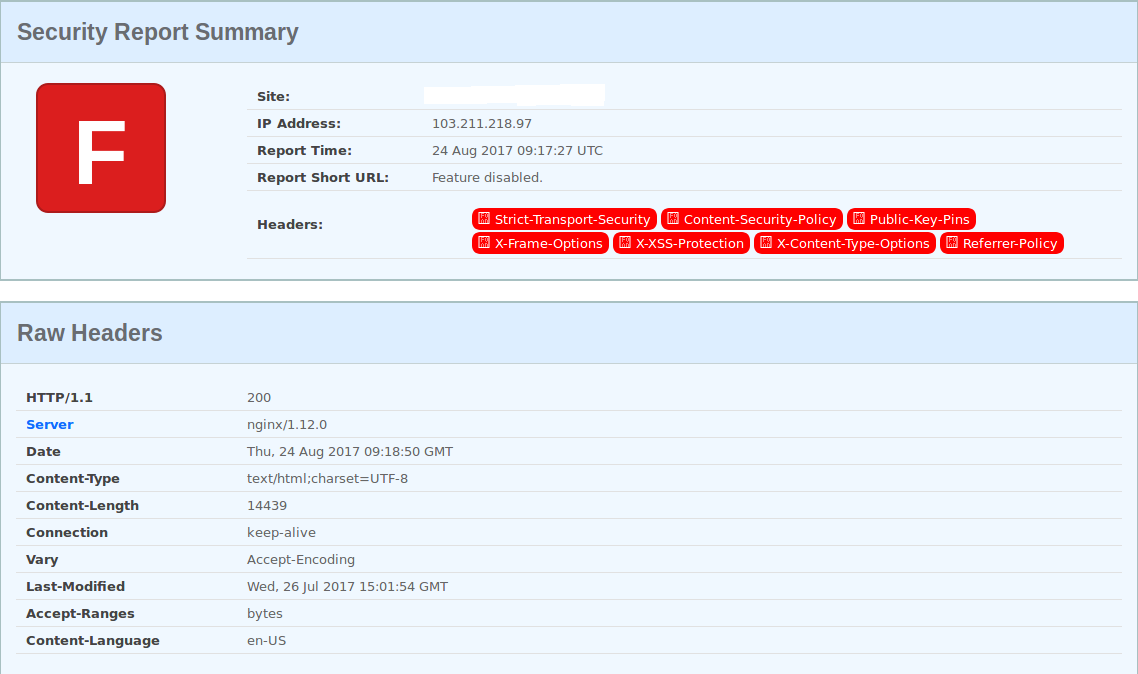
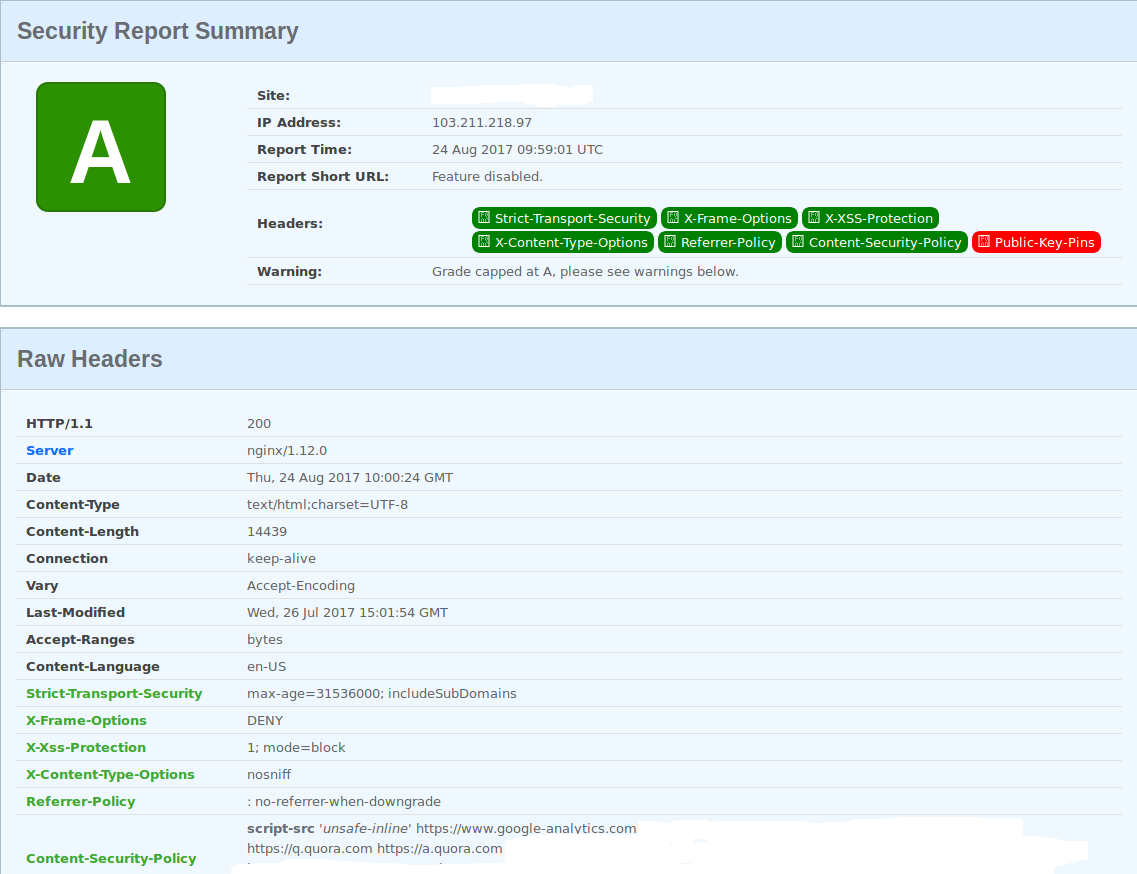
安全研究员 Scott Helme 贡献了一个非常棒的网站 [https://securityheaders.io/],可以分析自己站点的Header(报文头),并提出改进安全性的建议。示例如下(环境参数,Operating System: CentOS 7 ; haproxy 1.5.14 ; nginx 1.12.0)。
- 加固前的检测结果
- 加固后的检测结果
参考文献
- SSL Man-in-the-Middle Attacks|SANS Institute InfoSec Reading Room
- A new security header: Referrer Policy | Scott Helme
- 《Microsoft Developer Network:IE8 Security Part V: Comprehensive Protection》
- The WiFi Pineapple - Using Karma and SSLstrip to MiTM secure connections | Scott Helme
- Content Security Policy - An Introduction | Scott Helme
- Content Security Policy 入门教程 | 云栖社区
- Referrer Policy 介绍 | Jerry Qu